Intent Detection
What is Intent Detection?
Intent detection is use text to detect an intent that can be used start an action.
Language as Input
You can still capture intent regardless of language.
Language variations
- Synonyms
- two words that mean the same
- Near-synonyms
- two words that nearly or almost mean the same
- Generic/specific
- a word can have more specific names and vice versa a word can have more generic names
- ex. restaurant <-> cafe, bistro, coffee shop
- paraphrases
- sentences that can be said with multiple variations and have the same inherent meaning
- References
- intent that needs to be done based on current scenario
- "set an alarm six hours from now"
- "what is a good thai restaurant on my way back from work?"
- Errors
- Typographical
- how to map words that have spelling errors
- Transcription
- how to map sentences that have grammatical errors (because the language model or acoustic model did not transcribe the speech correctly)
- Typographical
- Negation
- negative intents
- "set school alarm for 7am everyday but not on weekends"
Language Representation
Language unit of interest
- Document > Paragraph > Sentence > Word > Prefix/Suffix
Lemmas
Lemmas take the root of words from sentences. For example: is -> be.
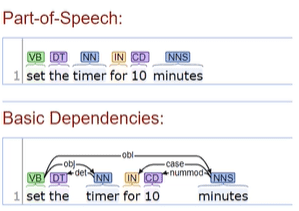
Part-Of-Speech (POS)
What the type of a word is: verb, noun, preposition, etc.
Named Entity Recognition
Recognize common names, companies (basically proper nouns) in sentences, and label the entity type (person, place, etc)
Syntactic Analysis
gives the dependencies for parts of speech
Word representation
Distributional Semantics
- Dense word representations which encapsulates their predictive nature of their context
- pre-trained (using larger corpora) and distributed
Newer representations such as BERT (Bidirectional Encoder Representation from Transformers), which provide a dense representation learned with (and triggered) a sentence.
Intent Classification
Steps
- Define the scope:
- Making sure the domain specified and not too broad.
- All intents that are not planned are deemed out-of-scope.

- What Languages will be supported?
- Define a list of intents
- Choose a methodolgy
Development
- Availability of data
- Development time
- Team's expertise
Production
- System's expected response time
- Adaptability
Template-based approach
Unsupervised (no training data required)
Still…. Requires to come up with a few template per intention.
Can always be used as a Baseline System.
Quick (enough) to develop.
Supervised ML Approach
Gather LOTS of GOOD data
- Balanced classes among all intents
- Multiple speakers/writers
- Spoken/Written sentences
- Erroneous sentences (spoken/written)
Existing packages (Python, other) allow quick enough development.
Takes a long time to train (requires GPUs)
Performance expectations: Train / Retrain, until… ?
Slot Filling
- Build a slot filler recognizer (classifier) for each intent.
- Make sure the features used to help the classifier don't limit it too much
- Example: word in address book as feature
- Decide what to do on optional slots not filled
- Which default to use?
- Choice of what to do when a filler is not recognized (internal):
- Assume it doesn't exist (apologize humbly)
- Suggest something close
- Example: Julianne, did you mean Julian?
- Suggest to fix the issue
- Example: Let's add Julianne in address book.
- Choice of what to do when a filler is not recognized (external):
- Assume it doesn't exist (apologize humbly)
- Suggest something close
- Example: did you mean Brady Ho?
- Suggest to fix the issue
- Example: “you can subscribe to the paying version of X music to listen to ….”
Approaches to slot filling
Values (slot filling)
- Accessibility to internal database
- Accessibility to external resources
- Accessibility to 3rd party providers
Internal database
- "Call Sarah"
- "Call Mom on speaker.“
- "Tell Lucy I am going to the store.“
- "Send email to John Doe about tomorrow and say Too busy to come.“
External Resources
- "What time is it in Tokyo?“
- "When is Labor Day?“
- “Turn on Bluetooth”
- “Where is the nearest hairdresser?”
- “Play music by Brad Meldhau.”
- "Check flight status of Air Canada 327”
- "What's the nearest museum?"
Iterative slot filling
We need to build a Focused Goal-Oriented Dialog
Purpose: Fill all the slots to proceed to the « Action » (do what is requested)
Hypothesis: Intent was correctly recognized!
UI design (Conversational design)
- Try not to annoy the user
- When possible, give options
- Will you drive, bike, take the train or take the bus?
- Keep user on track
Evaluation
Task to evaluate
- Slot Filling
- Check for errors when finding span and finding role
- Intent classifier
- errors could occur during classification
- wrong class
- wrong classification binary intent/out-of-scope
- wrong multi-class classification
In vivo / In vitro
- in vitro refers to the lab setting
- define metrics and benchmarks
- in vivo refers to in the real/wild
- users satisfaction
- model could work amazingly in vitro but poorly in vivo or vice versa
In Vitro Evaluation
Define benchmarks
- decide on task/subtask
- use (if possible) recognized datasets
- use recognized metrics
Metrics
Intent classification
- binary OOS/intent
- multiclass classification
precision/recall
- per class
- average over all classes
Depending on application, you decide what is valued more false-negatives or false-positives. Its hard to decide on this because you don't know what the user wants through in vitro testing
In Vivo Evaluation
Manage expectations
- explain scope
Limit frustration
- limit false positive or false negative
provide training to users
- sentence to be spoken (help speech recognition)
- provide request templates (typical sentences)
have good communication skills
- be apologetic