Intelligent Personal Assistant
Introduction
Intelligent Personal Assistant
This is software that can assist people with basic tasks, usually using natural language. Intelligent personal assistants can perform several tasks (internal commands, web access, Q/A, etc.). Either text or voice can trigger an action.
Voice Assistant
The key here is voice. A voice assistant is an intelligent personal assistant that uses voice recognition, speech synthesis, and natural language processing (NLP) to provide a service through a particular application.
Use of Voice assistants
Stand alone (internal commands)
- open facebook
- set the timer for 2 minutes
Application developed for the platform which can take voice commands (skills)
Web searches
- search for a thai restaurant in Ottawa
Factual Q/A
- Who is the prime minister of Canada ?
- What is the Coen brothers latest movie ?
Chatbot / Conversational Agent
Text is the main way to get assistance from a chatbot. Chatbots can simulate a conversation with a human user. Many companies use them in the customer service sector to answer basic questions and connect with a live person if necessary.
Intelligent Personal Assistant
- Simple dialog (linear/slot filling)
- Adaptability to the owner
Chatbot
- Often associated with a company (bank, reseller).
- The chatbot replaces a customer service or technical support person.
- More complex dialog with multiple speech turns.
Architecture and Wake Word Detection
Basic Architecture
- Wake word Detection
- Speech to test conversion, Automatic Speech Recognition (ASR)
- Intent Detection, Natural Language Detection (NLU)
- Action
- Answer Generation, Natural Language Generation (NLG)
- Speech synthesis, Text To Speech (TTS)
Wake word detection

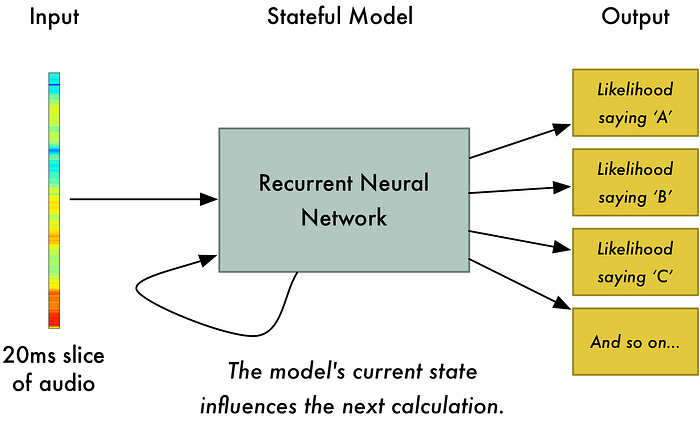
Automatic Speech Recognition
Machine Learning is used to learn words from speech signals.
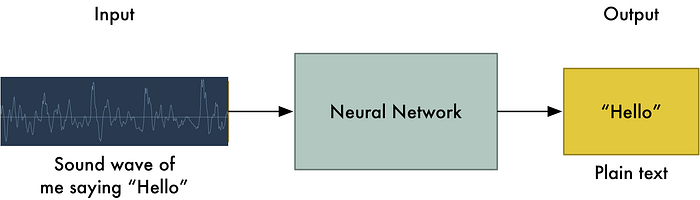
Frequency analysis is performed on each little slice of audio to learn the corresponding letters.
Characterizing elements
- Speaker
- Speaker's characteristic
- Age, gender, anatomy (vocal cords)
- Current state
- Level of stress, emotional state
- Language and culture
- American English, British English, Australian English
- Speaker's characteristic
- Utterance
- Utterance method
- Isolated words vs Connected words
- Utterance context
- Continuous Speech vs Spontaneous Speech
- Production characteristics
- Whisper vs normal voice vs scream
- Utterance method
- Discourse Content
- Domain
- The smaller the domain, the better the system performance (less ambiguity).
- Vocabulary:
- Small vocabulary - tens of words
- Medium vocabulary - hundreds of words
- Large vocabulary - thousands of words
- Very-large vocabulary - tens of thousands of words
- Domain
- Environment
- Surrounding sounds
- a clock ticking, a computer humming, a radio playing somewhere down the corridor, another human speaker in the background etc.
- Transducer
- Phone, Headset, Smart Speaker
- Channel variability
- Signal distortion (perhaps f- rom the transducer)
- Echo (maybe coming from the room
- Surrounding sounds
Intent Detection
Intent detection/classification is a problem of understanding the language (NLU).
NLU is very complex because the language is full of ambiguity (vague words, synonyms, paraphrases).
A "restaurant_search" intention can be expressed in different ways:
- I'm hungry!
- Show me some good pizza places
- I want to eat sushi with my friend
- Are there any good Italian restaurants near here?
Linear dialogs
Process of collecting all the necessary information to complete an action (e.g. booking an appointment or making an order).
Non-linear dialogs
Closer to a "real" conversation with branches, twists and turns, based on changes and context.
- Very complex to build
- Quickly become unmanageable after 4-5 speech turn
- Keeping track of the "state" is hard
- Which slots are filled
- Also, what was tried in the slots and failed
- users should be reminded - We tried 9pm before and it was unavailable
- Careful of looping
Hybrid chatbot with menus
If the conversation must lead to an action (fulfillment), we want to avoid multiple turns with the service that will provide the action. An alternative is an hybrid conversation agent which would sometimes give menu options.
Action
To execute the desired action could require:
- Access to internal commands
- Access to external suppliers
- Access to knowledge bases
- Access to search engines
Access to internal commands:
- Access to “standard” or added applications
- open facebook
- Skills (applications) developed by different people
- Internal commands
- set the timer for 2 minutes
- Other behavior
- Tell me a joke
Access to external suppliers:
- Simple tasks requiring a service provider (3rd party)
- What is the weather tomorrow ?
- Read the latest sport news on CBC
- Complex tasks requiring exchange of information with a service provider (3rd party)
- I want to reserve a table for 2 at Gezellig
Access to knowledge bases:
- Factual Q/A
- Who is the prime minister of Canada ?
- What is the Coen brothers latest movie ?
Access to search engines:
- Web searches
- search for a thai restaurant in Ottawa
- Factual Q/A (not answered by KB)
- Is there a vaccine for COVID-19?
Answer Generation
Generating a response
Types of answers:
- Complete answers pre-recorded (pre-coded).
- Answer templates with variables.
Complete pre-recorded answers
- Lists of stories or jokes.
- Tell me a joke.
- "Two guys who are going ....“
- Answers for smalltalk
- "Can I help you?".
- How are you?
- "I'm fine and you.“
- Answer of excuse
- "I do not understand your question.“
- Answer of accomplishment.
- “OK. Done”
Answer templates
- Replacing variables by the extracted entities (during intent detection)
- Play music by Brad Mehldau.
- Intent "play_music"
- Artist: Brad Mehldau
- Template: "Here's X's music."
- Instantiated template: "Here's Brad Mehldau's music."
- Play music by Brad Mehldau.
Example based on patterns for the weather
(A="It is", D="Tomorrow will be", M="Wednesday will be") a (sunny, cloudy, rainy) day and X degrees celsius.
Speech Synthesis
Speech synthesis is a form of output where a computer or other machine reads words to you out loud in a real or simulated voice played through a loudspeaker; the technology is often called text-to-speech (TTS).
Steps for Speech Synthesis
Pre-processing for disambiguation
Preprocessing involves going through the text and cleaning it up so the computer makes fewer mistakes when it actually reads the words aloud.
Things like numbers, dates, times, abbreviations, acronyms, and special characters (currency symbols and so on) need to be turned into words—and that's harder than it sounds.
Example: The number 1843 might refer to
- a quantity of items ("one thousand eight hundred and forty three")
- a year ("eighteen forty three")
- or a padlock combination ("one eight four three")
each of which is read out slightly differently.
Words to phonemes
Breaking words down into sounds
Phonemes to sounds
Concatenative Approach
Speech synthesizers that use recorded human voices have to be preloaded with little snippets of human sound they can rearrange.
In other words, a programmer has to record lots of examples of a person saying different things, break the spoken sentences into words and the words into phonemes.
If there are enough speech samples, the computer can rearrange the bits in any number of different ways to create entirely new words and sentences.
Modulation for intonation, volume
As any good actor can demonstrate, a sentence can be read in different ways depending on the meaning of the text, the person speaking and the emotions it wishes to express.
In linguistics, this idea is known as prosody and is one of the most difficult problems for voice synthesizers.